Explore the kidney stone symptoms in female patients and some causes, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Kidney stone symptoms in female patients are often very similar to those experienced by males, however they are sometimes overlooked or wrongly attributed to other causes in females.
Kidney stones are small, hard deposits of mineral and acid salts that form on the inner surface of the kidneys. In many instances, kidney stones do not cause any symptoms, however in cases where they are symptomatic, they can cause severe pain and discomfort.
This blog aims to explore the kidney stone symptoms in female patients and some causes, diagnosis, and treatment options.
What are Kidney Stones?
Kidney stones are small mineral deposits that form in the urinary tract. Stones may develop if the urine becomes too concentrated with certain substances. Types of kidney stones include calcium oxalate stones (most common), uric acid stones, struvite stones, and cystine stones. These present due to different causes and risk factors.
Kidney Stones Video:
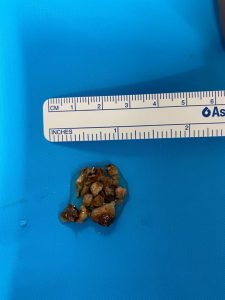
Fragmented Kidney Stone Removed from Patient:
Causes of Kidney Stones and Kidney Stone Symptoms in Female Patients
Before we take a look at kidney stone symptoms in females, we need to understand the causes of kidney stones.
The most common causes of kidney stones- and therefore kidney stone symptoms in female patients- include dehydration, some particular diets, obesity and some medical conditions. There are also some risk factors of women in general, such as pregnancy and the hormonal changes that come with it.
In general, a high-sodium diet combined with inadequate fluid intake and certain lifestyle factors also contribute to the overall risk of developing kidney stones.
General Symptoms of Kidney Stones vs Kidney Stone Symptoms in Females
As mentioned above, not all kidney stones cause symptoms; sometimes they are discovered incidentally. In cases where they do cause the patient symptoms, these can vary but often include:
- Severe pain and discomfort in the side and back (flank), below the ribs, and usually radiating to the lower abdomen and groin.
- Nausea and vomiting from the intense pain, or in cases where there is also infection present.
- A need to urinate frequently and urgently, often in small amounts.
- Blood in the urine, where blood appears pink, red, or brown.
Kidney stone symptoms in female patients may be slightly different. In addition to the general kidney stone symptoms, women may also experience:
- Lower abdominal pain: whilst men often report back pain, women may experience more lower abdominal pain.
- Symptoms during pregnancy: some women are at increased risk of developing kidney stones and unique symptoms due to changes in the urinary tract.
- Menstrual cycle impacts: some women report that kidney stone symptoms can coincide with their menstrual cycle, making it harder to differentiate between menstrual pain and kidney stone pain.
Diagnosing Kidney Stones in Women
Kidney stone symptoms in female patients may vary slightly from those in males, however for the majority of cases, the diagnostic process is the same:
- Physical Examination: the urologist will assess symptoms and medical history.
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasound, CT scans, and X-rays may be used to locate and identify the size of the stones.
- Urine and Blood Tests: These tests can detect high levels of minerals and other substances that cause stones.
Complications of Kidney Stones in Female Patients
Kidney stones that are symptomatic require treatment. If left untreated, kidney stones can lead to complications such as:
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Kidney stones can block the flow of urine through the urinary tract, leading to painful inflammation and infection.
- Kidney Damage: Persistent stones can cause damage to the kidneys due to pressure build up.
Treatment Options for Kidney Stone Symptoms in Female Patients
Treatment options for kidney stone symptoms in female patients are often the same as those offered to males, with this exception of pregnant women, who may require different treatments.
Treatment for each patient’s kidney stone symptoms will depend upon the size and type of stone and the severity of symptoms. Treatment is centered around:
- Pain management medications
- Medications to help stones pass through the urinary tract more easily
- Surgical interventions such as ureteroscopy, lithotripsy (using shock waves to break up stones), and percutaneous nephrolithotomy (removing stones through a small incision) may be necessary for larger stones.
When to Seek Medical Attention
No matter whether it is suspected kidney stone symptoms in female or male patients, it is important to seek prompt medical attention for diagnosis. This is especially important if you are experiencing severe pain, blood in your urine, or symptoms of a urinary tract infection (fever, chills, nausea or vomiting). Early diagnosis can prevent complications and make treatment more effective.
